Concepts
A queue is an ordered collection of tasks. A task is a unit of work (or a message) that carries a useful
payload. A payload is opaque to Moab, it can be end-to-end encrypted if needed.
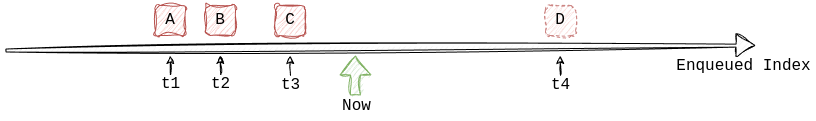
Internally, those tasks are indexed by several properties. The main index (Enqueued index) is ordered by scheduled_at
timestamp. Below, a task A is scheduled at a time t1, task B at t2 where t1 < t2, and so on:
Enqueuing
Enqueuing is adding a task to the queue. Moab queue is durable. If Enqueue returns a successful response it
guarantees all tasks have been persisted and replicated.
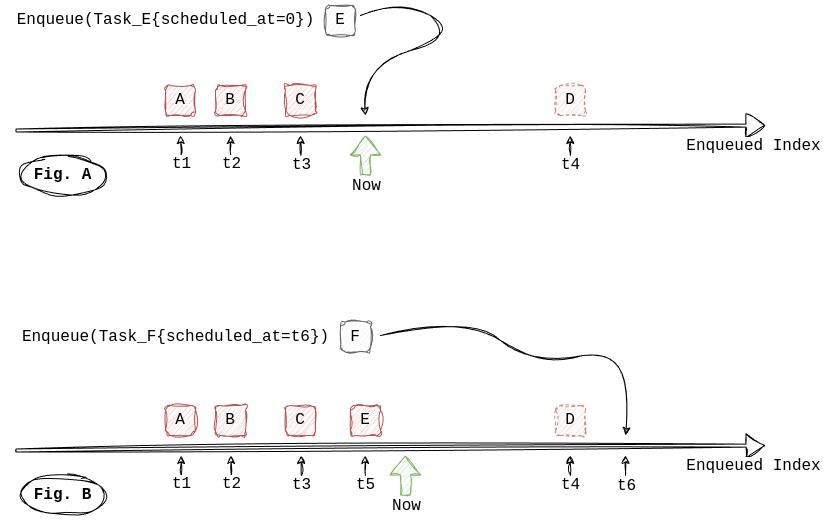
When enqueued, a task is in ENQUEUED state and is scheduled for now by default, meaning it is available for processing
immediately (Fig. A). A task can also be scheduled into the future (delayed) by explicitly specifying a
scheduled_at timestamp (Fig. B). If provided scheduled_at is in the past (scheduled_at < now) then it will be
replaced with now. The timestamp scheduled_at is not a unique property, several tasks can be scheduled at the same time.
Timestamp now is measured by API gateway servers, there might be drifts in time between those servers and the client, who
is enqueuing a task, or between servers themselves. Because of that, there is no guarantee that two consequent calls from
the same client will enqueue tasks in the same order. FIFO order is guaranteed outside any possible clock drift between
API gateway servers.
Dequeuing
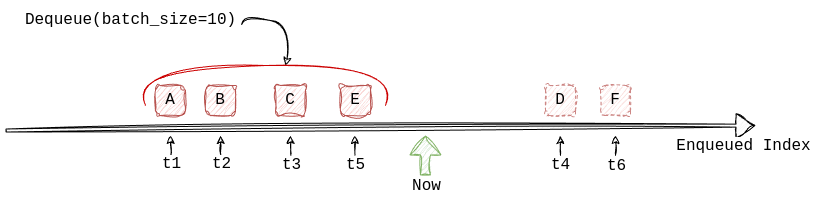
Dequeuing is picking up (pulling) a task from the queue. A worker is a program which periodically dequeues tasks and processes them (a consumer).
On dequeuing Moab returns only the tasks where scheduled_at <= now starting from the oldest tasks, so FIFO order is
maintained. A task can be dequeued only to a single worker and can never be delivered twice. Strictly speaking,
this is at most once delivery guarantee for each attempt.
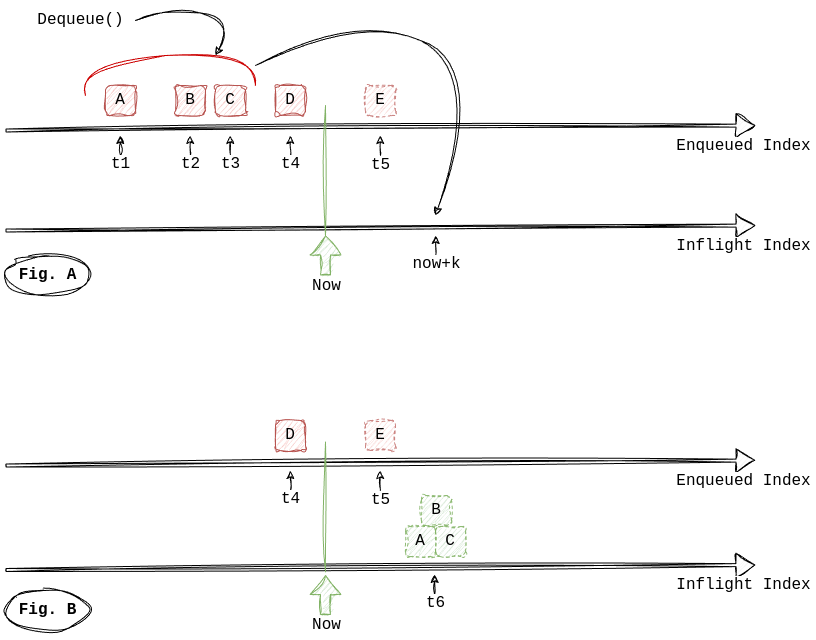
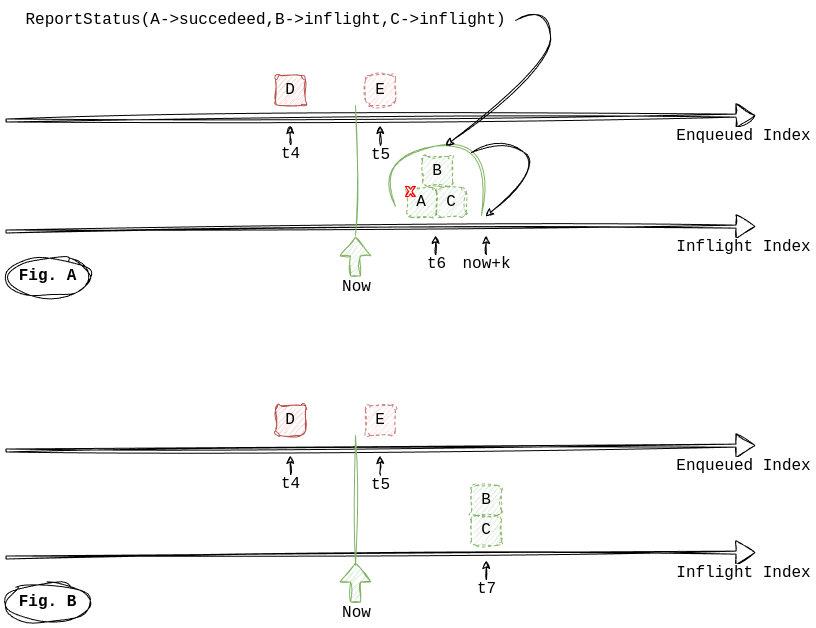
When dequeued, tasks go to INFLIGHT state and attempts = 1 indicates that it is picked up for the first time.
They are removed from the main index and added to Inflight index. A task is considered inflight for
keepalive_timeout_in_seconds period, so it is placed to the Inflight index at now + keepalive_timeout_in_seconds
position. Optional keepalive_timeout_in_seconds can be set in Enqueue request for each task individually, otherwise
a default keepalive_timeout_in_seconds from the queue will be used.
A worker must report a status of an inflight task within this keepalive_timeout_in_seconds period. A status report can
be any of:
SUCCEEDED- the worker has successfully processed this task.INFLIGHT- the worker is still processing this task. There is no upper limit for long-processing tasks as long as a worker is able to report status everykeepalive_timeout_in_seconds.FAILED- there was a failure while processing this task and the worker recognized this failure.
Succeeded tasks are removed from the queue. Inflight tasks are moved in Inflight index further to the next
keepalive_timeout_in_seconds. Failed tasks are retried.
If a worker is dead or for any reason has not reported any status within given timeout a task is considered FAILED. A
task has to be explicitly reported as SUCCEEDED in order to be deleted from the queue. This makes Moab resilient to
all sorts of failures (with network or workers). See Retries section for more details.